What is Output Noise?
The AC component that may be present on the DC output of a power supply. Switch-mode power supply output noise has two components: a lower frequency component at the switching frequency of the converter and a high-frequency component due to fast edges of the converter switching transitions. Noise should always be measured directly at the output terminals with a scope probe having an extremely short grounding lead.
The switched mode power supplies have become more common and widely used in most of the electronics equipment. They have replaced the traditional linear power supplies because of their higher efficiency, smaller sizes, and weight. However, the power supplies generate more noise compared to the linear supplies.
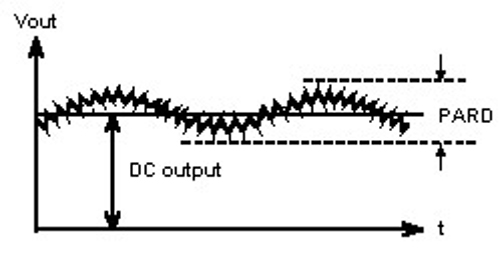
The output noise appears as a sine wave overlapping the output DC voltage.
Figure 1 Power supply output noise waveform – Image Credit
The SMPS will usually produce the narrowband spectral noise containing the fundamental switching frequency as well as higher order harmonics. However, the push-pull converters may produce a sub-harmonic component usually at the one-half of the switching frequency mostly due to the imperfect balance.
The output noise is made up of several different frequencies, such as the mains frequency, which can be 50 or 60 Hz, as well as other noises. In a supply using the FET switching transistor at high frequencies, the output noise may contain the narrow and sharp spikes, in addition to many high frequencies.
Sources of power supply output noise
The noise in the power supplies come from the non-ideal characteristics of the components. These become noise sources when subjected to the current and especially alternating currents. In switching devices such as the MOSFETS, the drain and source have some equivalent series inductances, Ld and Ls. These are usually indicated in the datasheets and must be considered during the design stages, typical values for a transistor such as the IRF7303 are 4nH for the drain and 6nH for the source.
On the other hand, the capacitors have leakage currents as well as the equivalent series resistance (ESR) which leads to noise when current flows through the capacitor. The circuit board design, traces and placement of components may also lead to noise when unwanted coupling occurs between the components.
The ERS is one of the main contributors of noise in capacitors, if this value is high, a current will drop some voltage and cause I2R losses, with the AC ripple contributing the most noise. As such, the capacitor selection must consider the ESR value.
The value of ESR is frequency dependent, and type of capacitor. Some manufacturers specify ESR value at certain frequencies while others do not. Either way, it might be necessary to determine the value if the operating frequency of the power supply is different from the specified.
Minimizing power supply output noise
Typical output noise is usually about 1% of the power supplies output voltage. When designing an SMPS, the output noise should be within the acceptable limits, otherwise, a high value can lead to circuit malfunctions and sometimes cause the sensitive systems to shut down.
Proper design and component selection
The amount of noise is greatly influenced by the choice of components such a switching transistors, diodes, filter capacitor, transformer. In addition, the circuit design, components layouts, PCB traces, and component quality determine the level of output noise. As such, a careful design and proper selection of components can help in minimizing the level of noise.
Output filter
The output noise can be reduced by applying an external output filter. However, it is important to determine or understand the nature of the output noise so as to know the type of a filter to use. This can be done by using an appropriate measurement method. Measuring the output noise is sometimes a challenge due to the wide bandwidth of the noise, but can be measured using an oscilloscope. However, care should be taken not to introduce more noise from the instrument’s probes.