A DIN Rail is a metal strip of standard dimensions originally defined in specifications published by Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN) in Germany, and since adopted as European (EN) and international (ISO) standards. It provides a convenient and fast method of assembling any combination of electrical and electronic devices into application-specific systems; these can be compact, yet fully functional.
Ease of assembly and extensive standardisation have made the DIN rail increasingly popular among industrial control, instrumentation and automation system builders, and hardware suppliers have responded by offering a wide choice of components. All aspects of industrial systems – terminals, signal conditioning, circuit breakers, relays, motor starters and even programmable logic controllers (PLCs) are available as components that can be simply snapped onto the rail to build up the configuration.
Among these components is an increasing range of AC-DC power supplies; below, we look at the points to consider when choosing suitable DIN rail mounting supplies for a control application.
1. Style and mechanical dimensions
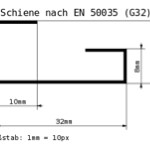
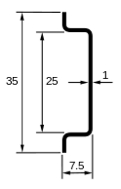
Fig.1: The three major types of DIN rail
As Fig.1 shows, there are three major types of DIN rail. The Top Hat type, which complies with EN 50022, BS 5584 and DIN 46277-3 is available with either a 7.5 mm depth as shown, or a 15 mm depth. The G Section meets EN 50035, BS 5825 and DIN 46277-1. The C Section is available as types C20, C30, C40 and C50, where the number suffix refers to the rail’s height in mm. Miniature (15 mm height) and 75 mm height top hat rails are also available.
Therefore the first point is to ensure that your power supply and DIN rails have compatible styles and dimensions. Power supplies, like circuit breakers, typically use Top Hat types, but it’s a point to be checked.
Designers working to minimise the size of their final system can benefit from Thin Width Profile DIN rail power supplies, now available with widths down to 32 mm. Thin Depth Profile products are also available.
2. Cooling method and working temperature range
DIN rail architecture is attractive partly because it facilitates assembly of very compact systems. Such systems are typically mounted onto a back plate and then into an enclosure providing environmental protection. The enclosure can be installed into an outdoor surveillance system, vehicle or other applications subject to temperature extremes.
It is therefore important to choose power supplies that do not need fans or forced air cooling, which would be difficult to set up in such embedded environments, as well as introducing another point of potential failure. It’s equally as important to consider the supply’s operating temperature range, bearing in mind the temperatures that could be reached within a sealed enclosure subject to external elevated temperatures; this enclosure often contains a dense population of hardware components generating additional heat, however efficient they may be.
The operating temperature range specification may also call for a minimum clearance area around the power supply to guarantee its validity. There may also be a derating curve to take into account. Even if operating in an excessive temperature does not cause the power supply to fail, it will shorten its life, especially if any internal electrolytic capacitors are overheated.
3. Protection types
DIN rail systems installed near their applications are expected to operate reliably and safely for extended periods of time without supervision – yet the power supplies within them can be subjected to potentially damaging events both from the incoming mains supply and the load they support. Accordingly, it’s important to specify DIN power supplies that are fully protected; ideally they should be protected against short circuit, overload, over temperature and over voltage.
The method of recovery from a fault situation should also be reviewed. For example some power supplies offer a ‘hiccup’ mode in which they will automatically resume operation if the fault is cleared, while others will need resetting or restarting to resume operation, even if the fault clears.
4. Fixed or adjustable output voltage, or fixed output current
In some applications such as test or development systems, the convenience and versatility of an adjustable DC voltage output is desirable or even essential. However, many other applications depend on a DC supply that remains fixed to ensure smooth operation. Many LED lighting installations require a fixed DC voltage supply to ensure that any fluctuations, outages, surges or changes to the current will not affect the LED output. This allows the LED lighting to maintain a predictable and reliable light intensity.
Some LED lighting applications, especially those operating strings of LEDs in series, operate at optimum efficiency if they are driven by a constant current rather than constant voltage power source. Constant current outputs are also useful for industrial applications where they allow the power supply output to remain stable during unexpected output surge current demands.
5. Connection and wiring
For loads of more than a few tens of mA, the cabling between the power supply and its load should be kept as short and as large in cross sectional area (CSA) as possible. This is to minimise I2R losses which can heat the cables as well as reducing the voltage across the load terminals. The AC wires to the power supply should also be as short and as large in CSA as possible, to minimise noise radiation.
The live and neutral AC input lines should be kept separate from the + and – DC output pair to minimise noise induction into the DC wiring. The AC pair and DC pair should each be twisted for the same reason.
6. Efficiency and no-load power consumption
If a power supply is installed into a compact DIN rail system comprising a densely-packed set of components in a confined space, power dissipated as heat must be kept to a minimum – especially if the system relies on convection cooling. Although dissipation can be improved if the enclosure can be used as a heatsink, it’s best to minimise it in the first place by choosing a power supply with high efficiency; 89% is a good value.
Minimal no-load power consumption also helps to reduce heat dissipation; power supplies with no-load consumption below 0.1 W are available.
7. Input voltage range
If the DIN rail system could potentially be operated in the UK, Europe, North America or maybe beyond, then a PSU with a universal AC input range of 80 – 264 Vac, together with a frequency range of 47-63 Hz, is required.
Another consideration is that some data and communications centres are starting to use DC power distribution systems to reduce transmission losses and achieve other savings. PSUs with DC input ranges such as 127 – 370 Vdc are available for direct connection into such power architectures. Battery systems?
8. Additional functionality and control signal contacts
Some DIN rail PSUs are available with additional functionality and/or signal contacts. One example is a DC UPS function in which the PSU provides an auxiliary DC output pair; this can be used to drive a charger and battery for implementing a DC UPS. Contacts on the PSU provide ‘AC OK’ and ‘Battery Low’ alarm signals.
PSUs with ORing diodes and input monitoring signals are another example of added functionality; these allow a 1+1 redundant PSU pair to be set up on the DIN rail.

9. Fixed switching frequency
In some noise-sensitive applications, it can be advantageous to specify a PSU with a fixed switching frequency of, say, 100 kHz. This allows designs to avoid interference with system clock frequencies.
10. UL 508 Industrial Control Equipment Standard
If the DIN rail system is intended for use in the USA (North America?) for controlling electric motors, its power supply and other components must comply with Underwriters’ Laboratory National/International Standard UL 508, the UL safety standard for industrial control equipment. Industrial Control Equipment means components such as selector switches, relays, contactors, motor starters, power supplies and other items used in relation to motor control. It also encompasses complex assembles such as programmable logic controllers containing such components.
UL 508 covers devices rated up to 1500 V, intended for use in an ambient temperature of 0 – 40°C, unless specifically indicated for use in other conditions.
Getting it absolutely right
“There can be other factors affecting the choice of a DIN rail PSU – like any other PSU – which depend on the application,” commented Andy Wall, CEO of Sunpower Technology. “The above examples, however, are a good representation of the topics raised by customers as they review our DIN rail power supply range. In any case, it always makes sense to discuss your target application with your PSU supplier. If he’s competent, he’ll not only offer you the best possible fit; he may well also advise you on issues that perhaps you had not yet considered during your decision-making process.”
Sunpower Din Rail Power Supplies
Sunpower manufactures a range of din rail power supplies. For more information please view our complete range.