What is Isolation Voltage?
The isolation voltage refers to the highest voltage that can be applied across a device for one second without compromising the isolation in the device. This refers to the amount of voltage between the power supply’s input and the supply’s output or chassis, above which, it would damage the power supply or cause some direct current (in microamps) to flow through an insulation.
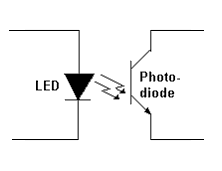
Isolation separates two parts of a circuit physically, ensuring that no direct current flows from one circuit to the other through the barrier. To achieve insulation, some components and circuits use safe insulating barriers provided by mediums such as an air gap, plastic, keep-out space on a PCB. In electronic circuits, the most commonly used isolation components use the following coupling methods to pass the signal from one circuit section to the other.
- Light in Optocouplers
- Magnetic flux in transformers
- Electrostatic field in capacitive couplers
Optical isolation – Image Credit
The level of insulation depends on factors such as the isolation voltage, transient voltage, air pollution and more. If it is required to have a high isolation voltage or voltage across the isolation barrier, then, a higher insulation is used.
When verifying the integrity of the isolation, a test voltage is usually applied across the input and output of component designed to provide isolation. The test ensures that a component such as an Optocoupler is able to survive a transient below the isolation voltage.
Significance of isolation voltage
Also referred to as the input to output isolation voltage, it represents the maximum voltage that can be applied across the Optocoupler, or other devices, and still maintain the electrical isolation. The isolation voltage can, therefore, be regarded as a measure of the insulation’s ability to withstand high transient voltages lasting only a few seconds.
Knowing the isolation voltage is usually necessary when a circuit has parts required to float above the ground or when there is a possibility of the load or equipment feeding a high voltage back into the power supply.
The isolation voltage, usually denoted by VISO, varies from one component and manufacturer to the other, as well as the application needs. It refers to the insulating material or barrier between the input and the output and may include the packaging technology in some applications. Typical values range from 750 V to over 7.5KV.
Determining the isolation voltage
The isolation voltage is determined by applying a test voltage across a component for a specified time. This is usually necessary in order to verify component’s ability to provide isolation when subjected to that amount of a transient voltage.
The test involves applying a high voltage across the device or equipment and observing if there is any leakage current across the insulation or barrier. The test duration is usually a short time of about 60 seconds. The test voltage is governed by the UL standards and given by VT = 2 • VISO(cont) + 1000.
Where VT is the test voltage and VISO(cont) the continuous voltage rating of the component under test.
The testing ensures that the device has adequate insulation that guarantees safety in case a breakdown occurs in the dielectric within the equipment or a high voltage spike such as that resulting from a lightning striking the power line. Users should not operate their equipment at the isolation voltage since this is usually required for safety testing as well as component or equipment specifications.